Code 32 – EGR voltage below closed limit
Let’s put on our Inspector Gadget propeller head beanies and think about how this works:
The EGR sensor is a variable resistor with ground on one leg and Vref (5 volts) on the other. Its’ resistance ranges from 4000 to 5500 Ohms measured between Vref & ground, depending on the sensor. The center connection of the variable resistor is the slider that moves in response to the amount of vacuum applied. The slider has some minimum value of resistance greater than 100 ohms so that the computer always sees a voltage present at its’ input. If the value was 0 ohms, there would be no voltage output. Then the computer would not be able to distinguish between a properly functioning sensor and one that had a broken wire or bad connection. The EGR I have in hand reads 700 Ohms between the slider (EPV) and ground (SIG RTN) at rest with no vacuum applied.
As vacuum is applied, the voltage on the slider increases (EVP). As the voltage increases, the computer knows the how much the EGR valve is opened and how much exhaust gas is being recirculated. It uses the load table to calculate the amount of exhaust gas required depending on RPM, Mass Air Flow, ACT, ECT & TPS. It then sends a signal to the Electronic Vacuum Regulator to hold, increase or decrease the vacuum being applied to the EGR valve.
Theory class is over now, let’s spin up our propeller head beanies and get with it… Go Gadget, Go…
Measure the resistance of the EGR sensor between the two end pins. You should see between 3500 to 5500 Ohms. With the sensor removed, measure the resistance again while pressing on the plunger. You should see the resistance drop from its high value to a low reading of 200-700 ohms depending on the sensor. No resistance readings, or values way out of range, the sensor is bad.
If the Orange white wire has Vref, (5 volts =/-.25 volt) then you have some wiring problems because the computer isn’t seeing the minimum voltage on the EVR pin. Ohm the wiring back to the computer. Check for resistance between the brown/lt green wire on the EGR sensor and pin 27 on the computer: you should have less than 1 ohm. Repeat the process for the orange/white wire and pin 26. Do it again between the black/white wire and pin 46. In no case should you have more than 1 ohm. Remember that resistance checks are always done with the power off the circuit.
Voltage and resistance checks are good: Here’s an EGR test procedure I copied from cjones
to check the EGR valve:
bring the engine to normal temp.
connect a vacuum pump to the EGR Valve
apply 5 in vacuum to the valve.
if engine stumbled or died then EGR Valve and passage(there is a passageway through the heads and intake) are good.
if engine did NOT stumble or die then either the EGR Valve is bad and/or the passage is blocked.
if engine stumbled, connect vacuum gauge to the hose coming off of the EGR Valve
snap throttle to 2500 RPM’s (remember snap the throttle don't hold it there).
did the vacuum gauge show about 5 in vacuum?
if not, check for manifold vacuum at the EGR vacuum valve.
if you have manifold vacuum then connect vacuum gauge to the EGR valve side of the vacuum valve and snap throttle to 2500 RPM’s.
should read about 5 in vacuum
End of cjones's test.
If the test procedure fails to provide proper vacuum, check vacuum feed lines for cracks & damage. If the vacuum lines are good, check the electrical wiring to the EVR. If the EVR electrical wiring is good, look for 12 volts on the red wire for the EVR. If the 12 volts is good, look for a varying voltage on the dark green wire on the EVR. Case of last resort, replace the EVR and then the computer
Code 63- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) signal too low TPS. Vref missing (5 volt reference voltage supplied by the computer), bad connections or damaged wiring, TPS sensor failed, TPS sensor way out of adjustment. Use a DVM to check for 5 volts on the Orange wire. If it is missing, look for +5 volts at the Orange wire on the EGR or MAP sensor located on the firewall near the center of the car.
All you need is less than 1.2 volt at idle and more than 4.25 at Wide Open Throttle (WOT). You'll need a Digital Voltmeter (DVM) to do the job.
When you installed the sensor make sure you place it on the peg right and then tighten it down properly. Loosen the back screw a tiny bit so the sensor can pivot and loosen the front screw enough so you can move it just a little in very small increments. I wouldn’t try to adjust it using marks. Set it at .6.v-.9 v.
1. Always adjust the TPS and Idle with the engine at operating temp. Dive it around for a bit if you can and get it nice and warm.
2. When you probe the leads of the TPS, do not use an engine ground, put the ground probe into the lead of the TPS. You should be connecting both meter probes to the TPS and not one to the TPS and the other to ground.
3. Always reset the computer whenever you adjust the TPS or clean/change any sensors. I just pull the battery lead for 10 minutes.
Code 11 - Computer's internal circuitry OK, passed internal self stest. No action requied for this code.
Code 21 – ECT sensor out of range. Broken or damaged wiring, bad ECT sensor.
Note that that if the outside air temp is below 50 degrees F that the test for the
ECT can be in error.
The ECT sensor has absolutely nothing to do with the temperature gauge. They are
different animals. The ECT sensor is normally located it the RH front of the engine in
the water feed tubes for the heater.
The ACT & ECT have the same thermistor, so the table values are the same
ACT & ECT test data:
Use Pin 46 on the computer for ground for both ECT & ACT to get most accurate
readings.
Pin 7 on the computer - ECT signal in. at 176 degrees F it should be .80 volts
Pin 25 on the computer - ACT signal in. at 50 degrees F it should be 3.5 volts. It is
a good number if the ACT is mounted in the inlet airbox. If it is mounted in the lower
intake manifold, the voltage readings will be lower because of the heat transfer.
Voltages may be measured across the ECT/ACT by probing the connector from
the rear. A pair of safety pins may be helpful in doing this. Use care in doing it
so that you don't damage the wiring or connector.
Here's the table :
50 degrees F = 3.52 v
68 degrees F = 3.02 v
86 degrees F = 2.62 v
104 degrees F = 2.16 v
122 degrees F = 1.72 v
140 degrees F = 1.35 v
158 degrees F = 1.04 v
176 degrees F = .80 v
194 degrees F = .61
212 degrees F = .47 v
230 degrees F = .36 v
248 degrees F = .28 v
Ohms measures at the computer with the computer disconnected, or at the sensor with the sensor disconnected.
50 degrees F = 58.75 K ohms
68 degrees F = 37.30 K ohms
86 degrees F = 27.27 K ohms
104 degrees F = 16.15 K ohms
122 degrees F = 10.97 K ohms
140 degrees F = 7.60 K ohms
158 degrees F = 5.37 K ohms
176 degrees F = 3.84 K ohms
194 degrees F = 2.80 K ohms
212 degrees F = 2.07 K ohms
230 degrees F = 1.55 K ohms
248 degrees F = 1.18 k ohms
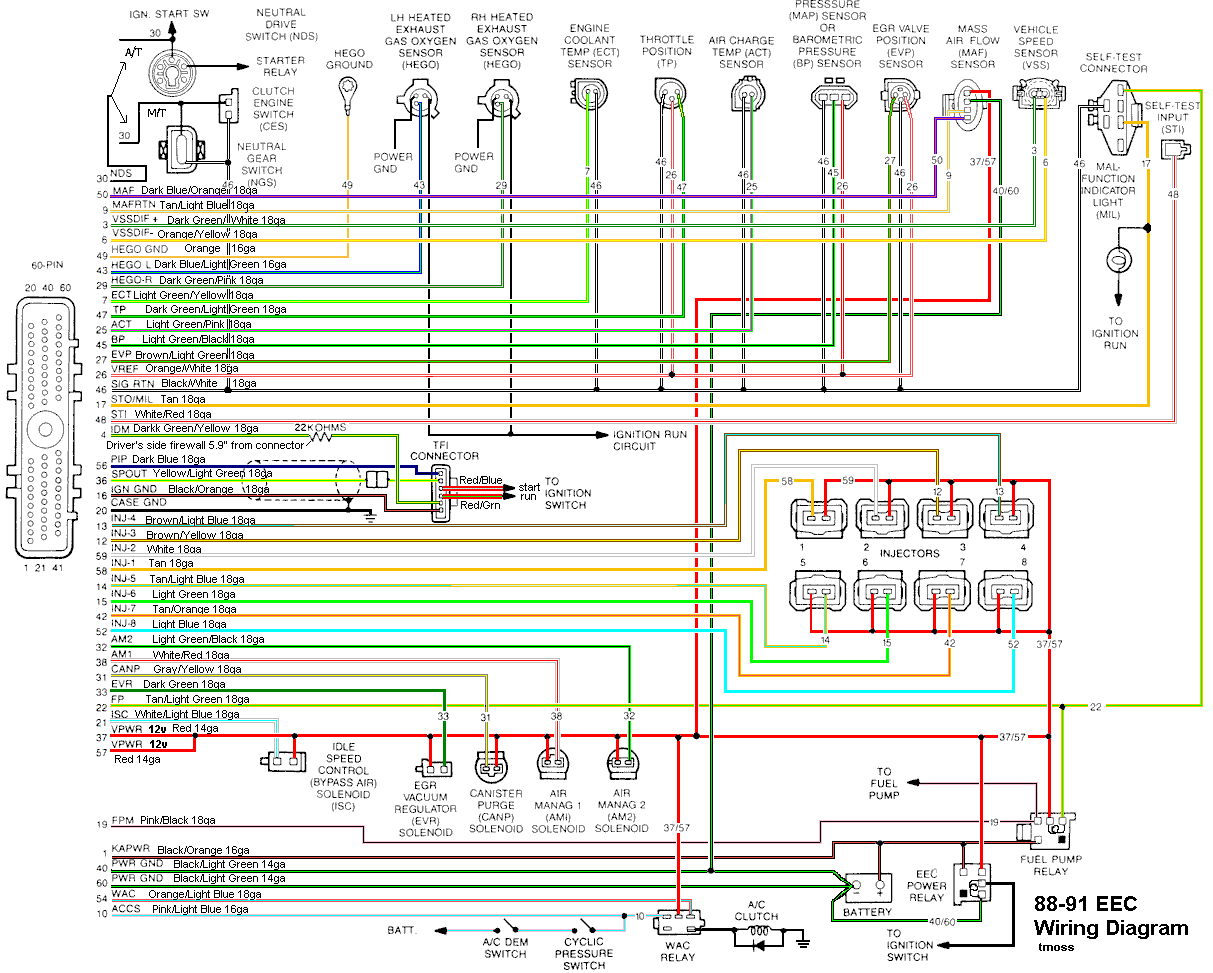
Diagram courtesy of Tmoss & Stang&2birds
See the following website for some help from Tmoss (diagram designer) & Stang&2Birds
(website host) for help on 88-95 wiring
Mustang FAQ - Engine Information
Ignition switch wiring
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/IgnitionSwitchWiring.gif
Fuel, alternator, A/C and ignition wiring
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/fuel-alt-links-ign-ac.gif
Complete computer, actuator & sensor wiring diagram for 88-91 Mass Air Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/88-91_5.0_EEC_Wiring_Diagram.gif
Vacuum diagram 89-93 Mustangs
http://www.veryuseful.com/mustang/tech/engine/images/mustangFoxFordVacuumDiagram.jpg
Code 41 or 91 - O2 indicates system lean. Look for a vacuum leak or failing O2 sensor.
Code 41 is a RH side sensor,
Code 91 is the LH side sensor.
The computer sees a lean mixture signal coming from the O2 sensors and tries to compensate by adding more fuel. Many times the end result is an engine that runs pig rich and stinks of unburned fuel.
The following is a Quote from Charles O. Probst, Ford fuel Injection & Electronic Engine control:
"When the mixture is lean, the exhaust gas has oxygen, about the same amount as the ambient air. So the sensor will generate less than 400 Millivolts. Remember lean = less voltage.
When the mixture is rich, there's less oxygen in the exhaust than in the ambient air , so voltage is generated between the two sides of the tip. The voltage is greater than 600 millivolts. Remember rich = more voltage.
Here's a tip: the newer the sensor, the more the voltage changes, swinging from as low as 0.1 volt to as much as 0.9 volt. As an oxygen sensor ages, the voltage changes get smaller and slower - the voltage change lags behind the change in exhaust gas oxygen.
Because the oxygen sensor generates its own voltage, never apply voltage and never measure resistance of the sensor circuit. To measure voltage signals, use an analog voltmeter with a high input impedance, at least 10 megohms. Remember, a digital voltmeter will average a changing voltage." End Quote
Testing the O2 sensors
Measuring the O2 sensor voltage at the computer will give you a good idea of how well they are working. You'll have to pull the passenger side kick panel off to gain access to the computer connector. Remove the plastic wiring cover to get to the back side of the wiring. Use a safety pin or paper clip to probe the connections from the rear. The computer pins are 29 (LH O2 with a dark green/pink wire) and 43 (RH O2 with a dark blue/pink wire). Use the ground next to the computer to ground the voltmeter. The O2 sensor voltage should switch between .2-.9 volt at idle.
Note that all resistance tests must be done with power off. Measuring resistance with a circuit powered on will give false readings and possibly damage the meter. Do not attempt to measure the resistance of the O2 sensors, it may damage them.
Testing the O2 sensor wiring harness
Most of the common multimeters have a resistance scale. Be sure the O2 sensors are disconnected and measure the resistance from the O2 sensor body harness to the pins on the computer.
The O2 sensor ground (orange wire with a ring terminal on it) is in the wiring harness for the fuel injection wiring. I grounded mine to one of the intake manifold bolts
Make sure you have the proper 3 wire O2 sensors. Only the 4 cylinder cars used a 4 wire sensor, which is not compatible with the V8 wiring harness.
Replace the O2 sensors in pairs if replacement is indicated. If one is weak or bad, the other one probably isn't far behind.
If you get only code 41 and have changed the sensor, look for vacuum leaks. This is especially true if you are having idle problems. The small plastic tubing is very brittle after many years of the heating it receives. Replace the tubing and check the PVC and the hoses connected to it.
A secondary problem with only a code 41 is for cars with an intact smog pump and cats. If the tube on the back of the heads clogs up the driver’s side, all the air from the smog pump gets dumped into one side. This excess air upsets the O2 sensor calibration and can set a false code 41. The cure is to remove the crossover tube and thoroughly clean the insides so that there is no carbon blocking the free flow of air to both heads.