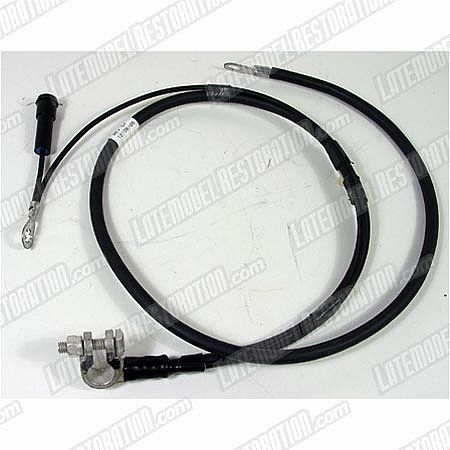
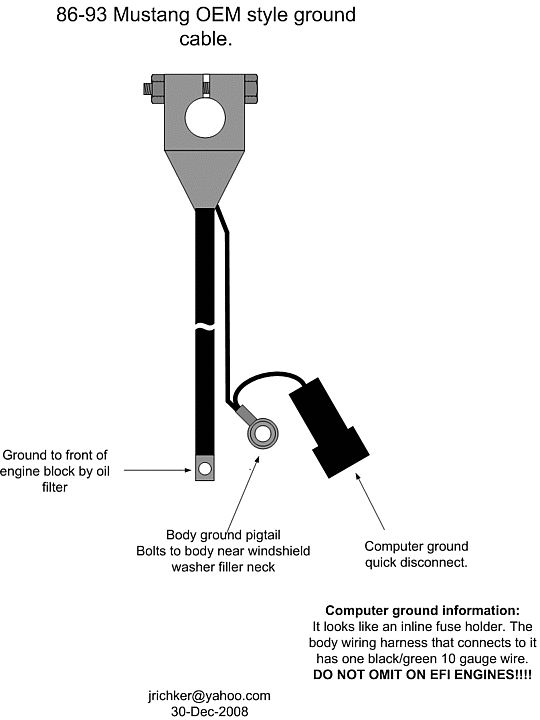
I just threw away a home-brewed cable that had failed--it was about 42" long and went more or less straight to the block, with a secondary neg. cable going to a ground next to the batt. on the fender. This was amateur-ish, so I tossed it, and bought a cable from NAPA, but it is 60" long and will need a secondary wire lengthened to fit.
Was there some specific route for the neg. cable or should I just wing it?
Was there some specific route for the neg. cable or should I just wing it?